|
Systems of Perspective
|
|
|
|
Implied orthogonal lines extend from viewer point
of view through the edges of established planes to create the illusion of distance and space, converging to a vanishing point placed on the horizon; dividing the planes into ground and sky. |
|
|
|
|

|
One Point Perspective:
A single point is placed on the horizon line and all the lines of objects at right
angles to the plane angle off toward that point: the object drawn appears parallel
with the picture plane. |
|
|
|
|
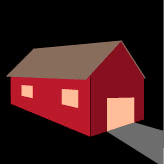
Two-Point Perspective:
A scene or object viewed from an angle which is not parallel to the picture plane:
the edges recede to two divergent points on the horizon line. |
|
|
|
|
Multi-Point Perspective:
An object is angular but also recedes upward or downward in space in relation to
the horizon line. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
![]()